Schistosomiasis (Bilharzia)
What is Bilharzia?
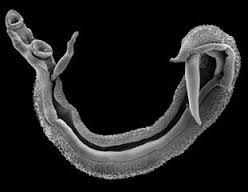
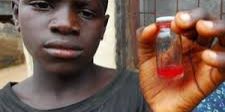
Bilharzia, or schistosomiasis, is a parasitic disease caused by worms called schistosomes. These worms live in the veins around the bladder or the intestines. There are two main types : urinary and intestinal schistosomiasis.
What Are the Key Signs and Symptoms of Bilharzia?
- Bloody urine (this is the clearest sign of urinary schistosomiasis. Boys usually notice this more easily than girls).
- Bloody stool.
- Frequent diarrhoea.
- Abdominal pains.
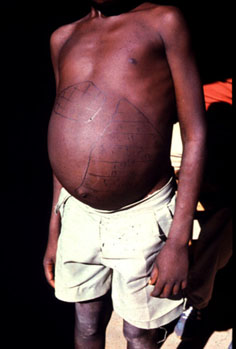
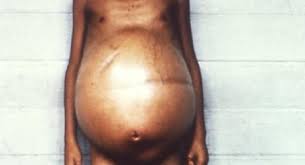
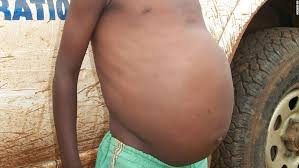
- Enlarged abdomen.
How Does Bilharzia Infection Take Place?
When someone who is infected defecates or urinates in water, the water becomes contaminated. Anyone who is then in contact with the water, for example when fishing or washing dishes or swimming, becomes infected.
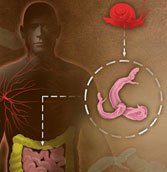
Infected individuals contaminate fresh water with urine or faeces containing schistosome eggs
In water, the miracidia hatch from eggs and contaminate snails (intermediate host). Snails later release large numbers of cercariae.
Cercariae contaminate individuals in contact with fresh water
What are the behavioural risk factors?
- Bathing or washing in rivers, lakes, ponds, etc.
- Fishing in fresh waters.
- Farming in swampy areas.
How Can One Avoid Getting Infected with Bilharzia?
- People should always use latrines instead of defecating or urinating in or near the water.
- Avoid contact with contaminated water.
- Wear boots in swampy areas.
- People who live in bilharzia endemic areas should be treated at least once a year.
How Do We Treat Bilharzia?
The most effective form of treatment is by administering the drug PRAZIQUANTEL, which is given by height using a tablet pole.
More pictures on schistosomiasis
Soil-transmitted Helminthiasis (STH)
What are Common Intestinal Worms?
Intestinal worms, also known as intestinal helminthes, are parasites that live in the human intestine for food and survival. There are 3 main types of common intestinal worms:
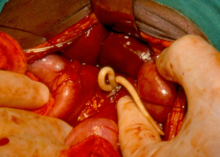
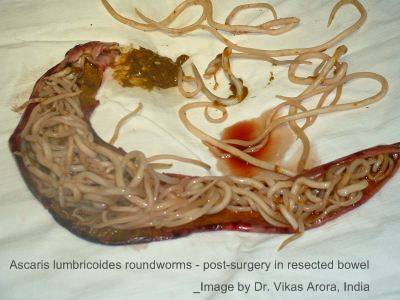
Roundworms
Whipworms
Hookworms
What are the Key Signs and Symptoms?
- Frequent diarrhoea
- Abdominal pains
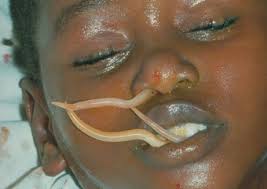
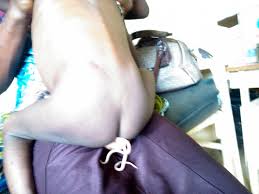
- Worms in the faeces
- Loss of energy and always being tired
- Loss of appetite and weight
- Itching.
How Does Infection with Intestinal Worms Take Place?
Intestinal worms occur wherever there is poor sanitation and a tropical environment. The route of infection begins with eggs in human faeces contaminating the soil. Infected individual contaminates the soil with faeces containing helminth eggs. Eggs develop in the soil.
Other people are infected when they ingest the eggs from unwashed food and hands (in the case of roundworms and whipworms), or by parasite larvae penetrating the skin (in the case of hookworms).
In infected individuals, eggs or larvae develop into adult worms, which produce large quantities of eggs.
worminfection
What Are the Behavioural Risks for Intestinal Worms?
- Swallowing worm eggs from unwashed hands, fruits or vegetables.
- Drinking water which is contaminated with the eggs.
- Walking barefoot outside.
How Can One Avoid Getting Infected with Intestinal Worms?
- Always use the latrine and wash your hands afterwards.
- W ash all vegetables and fruits properly before you eat them.
- Wash your hands before eating.
- Wear shoes whenever you go outside.
- Treat infected people.
How do we treat these worms?
MEBENDAZOLE (500 mg) or ALBENDAZOLE (400 mg) for the treatment of intestinal worms. These drugs are given on single dose and easy to administer.